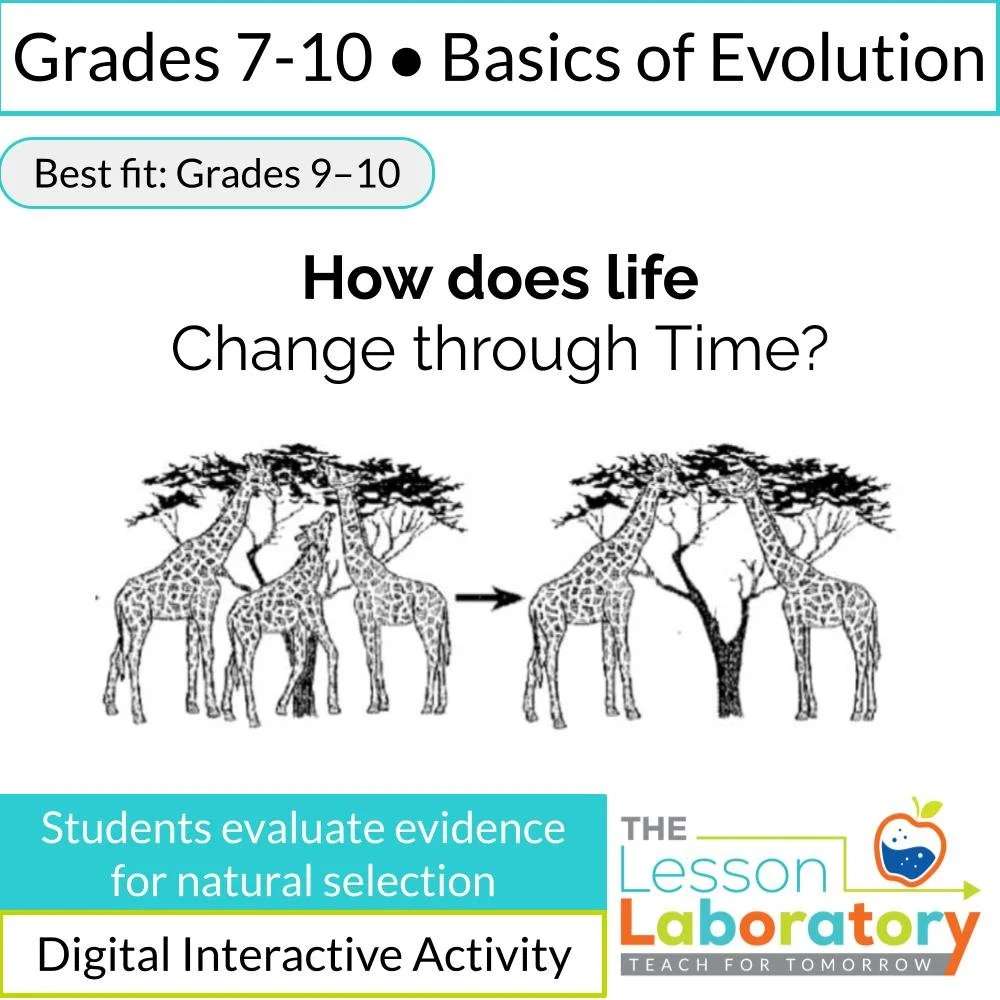



How Does Life Change Through Time? | Natural Selection vs. Other Claims
Evaluating Lamarck, Darwin, and Intelligent Design Using Evidence.
Revolutionize Your Learning Experience: This Google Slides lesson is excellently designed to be the gateway to your exploration of evolution. Dive into a thought-provoking session that challenges students to delve into the philosophy of science, empowering them to discern between scientific ideas and unsupported claims.
Unveiling the Scientific Method:
Foundations of Science: Begin by understanding the essence of scientific inquiry – it must be testable and grounded in evidence. Engage with four thought-provoking statements, discerning which qualify as true science.
Evidence for Evolution: Leverage previous knowledge as students compile a compelling list of evidence supporting the concept of evolution – the unifying principle of change over time.
Long Necks and Evolutionary Visionaries: Explore the perspectives of Lamarck, Darwin, and Behe, dissecting how each might elucidate the intriguing phenomenon of giraffes' long necks.
Deciphering Adaptations: Further distinguish these theories by unraveling how each would rationalize four captivating adaptations: cheetah speed, sperm whale lung capacity, butterfly spots, and octopus intelligence.
Testing Lamarck's Claims: Scrutinize the evidence and determine if it supports or counters Lamarck's assertions. Articulate your reasoning and ascertain whether Lamarck's ideas align with the scientific method.
Evaluating Darwin's Insights: Analyze the evidence and assess if it bolsters or undermines Darwin's propositions. Justify your assessments and conclude whether Darwin's ideas stand the test of scientific scrutiny.
Contemplating Intelligent Design: Examine the evidence and judge if it substantiates or challenges Behe's theories regarding intelligent design. Elucidate your analyses and make a determination on the scientific validity of Behe's concepts.
The Science of Selection: Conclude your exploration with a resounding realization - among Lamarckism, natural selection, and intelligent design, only Darwin's ideas emerge as truly scientific, grounded in testable concepts and supported by evidence.
Empowering Critical Thinking: This lesson transcends rote learning, fostering a deep understanding of evolutionary science and the fundamental principles that underpin scientific inquiry.
Begin Your Evolutionary Quest: Thank you for choosing us as your partners in scientific discovery. Embrace this enlightening journey, and watch as your students' understanding of evolution reaches new heights. Happy learning!
Grade & Course Recommendation:
Middle School:Grade 8 Advanced Life Science, introducing natural selection and historical theories.
High School:Grade 9–10 Biology, evolution and evidence unit.
To preview this lesson, click here.
Cross-Curricular Connections:
History of Science: Traces the progression of scientific thought about evolution.
ELA Integration: Encourages persuasive and evidence-based writing.
Philosophy / Social Studies Integration: Promotes respectful comparison of scientific and cultural perspectives.
Daily slide + literacy - based exit ticket included with purchase
Join the Lesson Laboratory and Teach for Tomorrow!
NGSS (Next Generation Science Standards)
High School NGSS Alignment
HS-LS4-1: Communicate scientific information that common ancestry and biological evolution are supported by multiple lines of empirical evidence.
Connection: Students analyze fossil, anatomical, and genetic evidence to explain species change over time.HS-LS4-2: Construct an explanation based on evidence that the process of evolution primarily results from genetic variation and natural selection.
Connection: Students distinguish between Lamarckian and Darwinian mechanisms for change.HS-LS4-3: Apply concepts of statistics and probability to support explanations that organisms with advantageous heritable traits tend to increase in proportion to those lacking the traits.
Connection: Students interpret population examples like the peppered moth and antibiotic resistance.HS-LS4-4: Construct an explanation based on evidence for how natural selection leads to adaptation of populations.
Connection: Students evaluate natural selection scenarios and how environmental pressures shape populations.
Science & Engineering Practices:
Analyzing and interpreting data
Constructing explanations
Engaging in argument from evidence
Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information
Crosscutting Concepts:
Cause and effect
Stability and change
Patterns
Common Core Standards
Grades 9–12:
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.1 / RST.11-12.1: Cite specific textual or visual evidence to support analysis of scientific explanations. (Students reference fossil data, anatomical evidence, and examples from provided texts.)
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.8 / RST.11-12.8: Assess the reasoning and evidence behind scientific claims. (Students critique Lamarck’s, Darwin’s, and Behe’s claims for validity and testability.)
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.9 / RST.11-12.9: Synthesize information from diverse sources to understand scientific ideas. (Students integrate examples from multiple types of evidence.)
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.WHST.9-10.1 / WHST.11-12.1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. (If students justify which theory is best supported by evidence.)
Evaluating Lamarck, Darwin, and Intelligent Design Using Evidence.
Revolutionize Your Learning Experience: This Google Slides lesson is excellently designed to be the gateway to your exploration of evolution. Dive into a thought-provoking session that challenges students to delve into the philosophy of science, empowering them to discern between scientific ideas and unsupported claims.
Unveiling the Scientific Method:
Foundations of Science: Begin by understanding the essence of scientific inquiry – it must be testable and grounded in evidence. Engage with four thought-provoking statements, discerning which qualify as true science.
Evidence for Evolution: Leverage previous knowledge as students compile a compelling list of evidence supporting the concept of evolution – the unifying principle of change over time.
Long Necks and Evolutionary Visionaries: Explore the perspectives of Lamarck, Darwin, and Behe, dissecting how each might elucidate the intriguing phenomenon of giraffes' long necks.
Deciphering Adaptations: Further distinguish these theories by unraveling how each would rationalize four captivating adaptations: cheetah speed, sperm whale lung capacity, butterfly spots, and octopus intelligence.
Testing Lamarck's Claims: Scrutinize the evidence and determine if it supports or counters Lamarck's assertions. Articulate your reasoning and ascertain whether Lamarck's ideas align with the scientific method.
Evaluating Darwin's Insights: Analyze the evidence and assess if it bolsters or undermines Darwin's propositions. Justify your assessments and conclude whether Darwin's ideas stand the test of scientific scrutiny.
Contemplating Intelligent Design: Examine the evidence and judge if it substantiates or challenges Behe's theories regarding intelligent design. Elucidate your analyses and make a determination on the scientific validity of Behe's concepts.
The Science of Selection: Conclude your exploration with a resounding realization - among Lamarckism, natural selection, and intelligent design, only Darwin's ideas emerge as truly scientific, grounded in testable concepts and supported by evidence.
Empowering Critical Thinking: This lesson transcends rote learning, fostering a deep understanding of evolutionary science and the fundamental principles that underpin scientific inquiry.
Begin Your Evolutionary Quest: Thank you for choosing us as your partners in scientific discovery. Embrace this enlightening journey, and watch as your students' understanding of evolution reaches new heights. Happy learning!
Grade & Course Recommendation:
Middle School:Grade 8 Advanced Life Science, introducing natural selection and historical theories.
High School:Grade 9–10 Biology, evolution and evidence unit.
To preview this lesson, click here.
Cross-Curricular Connections:
History of Science: Traces the progression of scientific thought about evolution.
ELA Integration: Encourages persuasive and evidence-based writing.
Philosophy / Social Studies Integration: Promotes respectful comparison of scientific and cultural perspectives.
Daily slide + literacy - based exit ticket included with purchase
Join the Lesson Laboratory and Teach for Tomorrow!
NGSS (Next Generation Science Standards)
High School NGSS Alignment
HS-LS4-1: Communicate scientific information that common ancestry and biological evolution are supported by multiple lines of empirical evidence.
Connection: Students analyze fossil, anatomical, and genetic evidence to explain species change over time.HS-LS4-2: Construct an explanation based on evidence that the process of evolution primarily results from genetic variation and natural selection.
Connection: Students distinguish between Lamarckian and Darwinian mechanisms for change.HS-LS4-3: Apply concepts of statistics and probability to support explanations that organisms with advantageous heritable traits tend to increase in proportion to those lacking the traits.
Connection: Students interpret population examples like the peppered moth and antibiotic resistance.HS-LS4-4: Construct an explanation based on evidence for how natural selection leads to adaptation of populations.
Connection: Students evaluate natural selection scenarios and how environmental pressures shape populations.
Science & Engineering Practices:
Analyzing and interpreting data
Constructing explanations
Engaging in argument from evidence
Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information
Crosscutting Concepts:
Cause and effect
Stability and change
Patterns
Common Core Standards
Grades 9–12:
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.1 / RST.11-12.1: Cite specific textual or visual evidence to support analysis of scientific explanations. (Students reference fossil data, anatomical evidence, and examples from provided texts.)
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.8 / RST.11-12.8: Assess the reasoning and evidence behind scientific claims. (Students critique Lamarck’s, Darwin’s, and Behe’s claims for validity and testability.)
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.9 / RST.11-12.9: Synthesize information from diverse sources to understand scientific ideas. (Students integrate examples from multiple types of evidence.)
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.WHST.9-10.1 / WHST.11-12.1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. (If students justify which theory is best supported by evidence.)